二、选择器
作用:选择页面上的某一个元素或者某一类元素
2-1、基本选择器
优先级:id>class>标签
标签选择器:选择一类标签(标签{})
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
/*标签选择器,会选择到页面上所有这个标签的元素*/
h1{
color: #030e0c;
background: cornflowerblue;
border-radius: 24px;
}
p{
font-size: 80px;
}
</style></head><body><h1>天水姜伯约</h1><h1>天水姜伯约</h1><p>你好</p></body></html>
类选择器 class:选择所有属性一致的标签,可跨标签(.类名{})
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
/*类选择器的格式 .class的名称
优点:可以多个标签归类,是同一个class,可以复用
*/
.boyue{
color: cornflowerblue;
}
.jiang{
color: red;
}
</style></head><body><h1 class="boyue">姜维</h1><h1 class="jiang">姜伯约</h1><h1 class="boyue">你好</h1><p class="jiang">早上好</p></body></html>
Id选择器:全局唯一(#id{})
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
/*id选择器:id必须保证全局唯一
#id名称{}
不遵循就近原则,固定的
优先级:id选择器> class选择器> 标签选择器
*/
#by{
color: aqua;
}
.style01{
color: red;
}
</style></head><body><h1 id="by">天</h1><h1 class="style01">水</h1><h1 class="style01">姜</h1><h1>伯</h1><h1>约</h1></body></html>
2-2、层次选择器
后代选择器:在某个元素的后面(祖爷爷 爷爷 爸爸 你)
/*后代选择器*/body p{
background: red;}
子选择器:一代,儿子
/*子选择器*/body>p{
background: aqua;}
相邻兄弟选择器
/*相邻兄弟选择器,只有一个相邻(向下选择)*/.active + p{
background: darkblue;}
通用选择器
/*通用兄弟选择器,当前选中元素的向下的所有兄弟元素*/.active~p{
background: aquamarine;}
2-3、结构伪类选择器
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<!--避免使用,class,id选择器-->
<style> /*ul的第一个元素*/
ul li:first-child{
background: aquamarine;
}
/*ul的最后一个元素*/
ul li:last-child{
background: red;
}
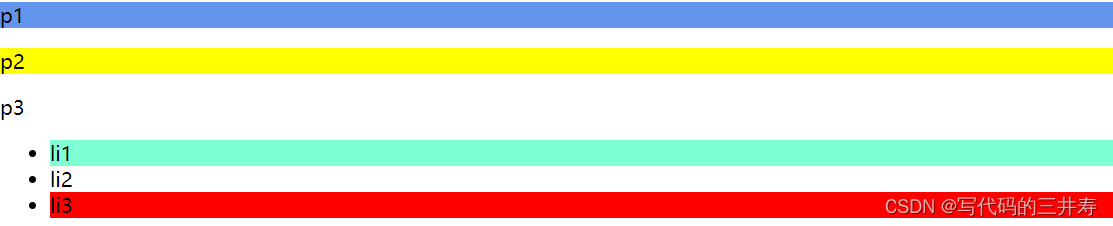
/*选中 p1:定位到父元素,选择当前的第一个元素
选择当前p元素的父元素,选中父元素的第一个,并且是当前元素才生效
*/
p:nth-child(1){
background: cornflowerblue;
}
/*选中父元素下的p元素的第二个*/
p:nth-of-type(2){
background: yellow;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>p1</p>
<p>p2</p>
<p>p3</p>
<ul>
<li>li1</li>
<li>li2</li>
<li>li3</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
2-4、属性选择器(常用)
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
.demo a{
float: left;
display: block;
height: 50px;
width: 50px;
border-radius: 10px;
background: blue;
text-align: center;
color: gainsboro;
text-decoration: none;
margin-right: 5px;
font: bold 20px/50px Arial;
}
/*属性名, 属性名 = 属性值(正则)
= 绝对等于
*= 包含这个元素
^= 以这个开头
$= 以这个结尾
*/
/*存在id属性的元素 a[]{}*/
/*a[id]{
background: yellow;
}*/
/*id=first元素*/
/*a[id=first]{
background: green;
}*/
/*class 中有link的元素*/
/*a[class *= "link"]{
background: red;
}*/
/*选中href中以http开头的元素*/
/*a[href^=http]{
background: green;
}*/
a[href$=pdf]{
background: red;
}
</style></head><body><p class="demo">
<a href="http://www.baidu.com" class="link item first" id="first">1</a>
<a href="" class="link item active" target="_blank" title="test">2</a>
<a href="images/1.html" class="link item">3</a>
<a href="images/1.png" class="link item">4</a>
<a href="images/1.jpg" class="link item">5</a>
<a href="abc" class="link item">6</a>
<a href="/a.pdf" class="link item">7</a>
<a href="/abc.pdf" class="link item">8</a>
<a href="abc.doc" class="link item">9</a>
<a href="abcd.doc" class="link item last">10</a></p></body></html>

链接:https://blog.csdn.net/clover_page/article/details/130100672
作者:姜伯約